什么是Shiro
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
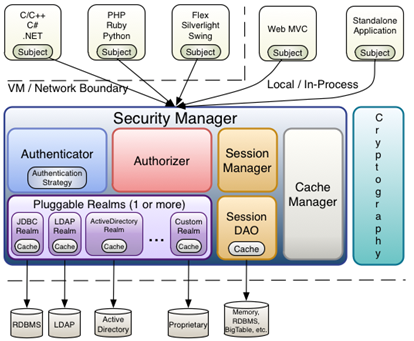
架构图
 概念
概念

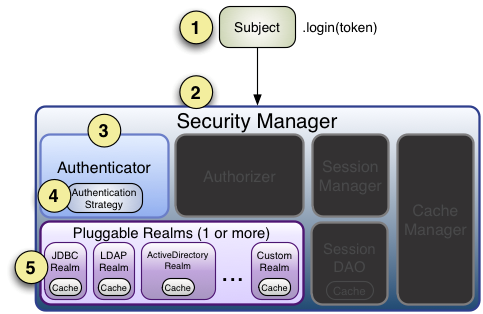
身份验证,即在应用中谁能证明他就是他本人。一般提供如他们的身份 ID 一些标识信息来表明他就是他本人,如提供身份证,用户名 / 密码来证明。
在 shiro 中,用户需要提供 principals (身份)和 credentials(证明)给 shiro,从而应用能验证用户身份:
principals:身份,即主体的标识属性,可以是任何东西,如用户名、邮箱等,唯一即可。一个主体可以有多个 principals,但只有一个 Primary principals,一般是用户名 / 密码 / 手机号。
credentials:证明 / 凭证,即只有主体知道的安全值,如密码 / 数字证书等。
最常见的 principals 和 credentials 组合就是用户名 / 密码了。接下来先进行一个基本的身份认证。
另外两个相关的概念是之前提到的 Subject 及 Realm,分别是主体及验证主体的数据源。
Realm:域,Shiro 从从 Realm 获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说 SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从 Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从 Realm 得到用户相应的角色 / 权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把 Realm 看成 DataSource,即安全数据源。如我们之前的 ini 配置方式将使用 org.apache.shiro.realm.text.IniRealm。
流程图如下:
 案例一
案例一

1.在Idea中创建Maven项目
2.导入Maven
pom.xml
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>3.编写测试类
AuthenticationTest.java
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
package com.benzhu.test;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.SimpleAccountRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class AuthenticationTest {
SimpleAccountRealm simpleAccountRealm = new SimpleAccountRealm();
public void addUser(){
//放入一个realm用来认证
simpleAccountRealm.addAccount("BenZhu","123456");
}
public void tsetAuthentication(){
//1.构建SecurityManager环境
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(simpleAccountRealm);
//2.主体提交认证请求
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("BenZhu","123456");
try {
subject.login(token);
}catch (AuthenticationException e){
System.out.println("验证失败!");
}
System.out.println("isAuthenticated:"+subject.isAuthenticated());
subject.logout();
System.out.println("isAuthenticated:"+subject.isAuthenticated());
}
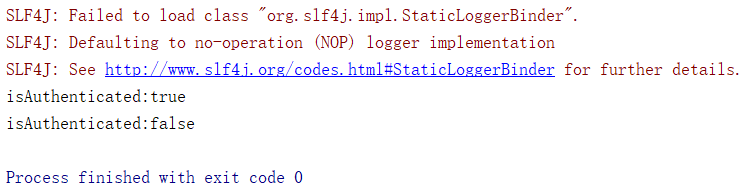
}4.效果图
案例二 数据放在配置文件
1.添加Maven
pom.xml
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
<!– shiro的依赖包 –>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version>
</dependency>2.添加数据文件
shiro.ini
- 01
- 02
- 03
[users]
zhang=123
wang=1233.编写测试文件
DemoApplicationTests.java
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
package com.benzhu.demo;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
public class DemoApplicationTests {
public void contextLoads() {
//1、获取SecurityManager工厂,此处使用Ini配置文件初始化 SecurityManager
Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory =
new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//2、得到SecurityManager实例 并绑定给SecurityUtils
org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//3、得到Subject及创建用户名/密码身份验证Token(即用户身份/凭证)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("benzhu", "123");
try {
//4、登录,即身份验证
subject.login(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
System.out.println("验证失败!");
//5、身份验证失败
}
System.out.println("11111!");
Assert.assertEquals(true, subject.isAuthenticated()); //断言用户已经登录
//6、退出
subject.logout();
}
}案例三 Reaml数据
1.创建Reaml
BenZhu1.java
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
package com.benzhu.demo.realm;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
public class BenZhu1 implements Realm {
public String getName() {
return "benzhu1";
}
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
//仅支持UsernamePasswordToken类型的Token
return token instanceof UsernamePasswordToken;
}
public AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = (String)token.getPrincipal(); //得到用户名
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials()); //得到密码
if(!"zhang".equals(username)) {
System.out.println("BenZhu1–用户名错误");
throw new UnknownAccountException(); //如果用户名错误
}
if(!"123".equals(password)) {
System.out.println("BenZhu1–密码错误");
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(); //如果密码错误
}
//如果身份认证验证成功,返回一个AuthenticationInfo实现;
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, password, getName());
}
}BenZhu2.java
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
package com.benzhu.demo.realm;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm;
public class BenZhu2 implements Realm {
public String getName() {
return "benzhu2";
}
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
//仅支持UsernamePasswordToken类型的Token
return token instanceof UsernamePasswordToken;
}
public AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = (String)token.getPrincipal(); //得到用户名
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials()); //得到密码
if(!"benzhu".equals(username)) {
System.out.println("BenZhu2–用户名错误");
throw new UnknownAccountException(); //如果用户名错误
}
if(!"123".equals(password)) {
System.out.println("BenZhu2–密码错误");
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(); //如果密码错误
}
//如果身份认证验证成功,返回一个AuthenticationInfo实现;
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, password, getName());
}
}2.配置文件ini
shiro-realm.ini
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
#创建一个realm
benZhu1=com.benzhu.demo.realm.BenZhu1
benzhu2=com.benzhu.demo.realm.BenZhu2
#指定securityManager的realms实现
#如果只有一个realm就写securityManager.realms=$benZhu1就好
securityManager.realms=$benZhu1,$benzhu23.测试文件
DemoApplicationTests.java
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
package com.benzhu.demo;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
public class DemoApplicationTests {
public void contextLoads() {
//1、获取SecurityManager工厂,此处使用Ini配置文件初始化 SecurityManager
Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory =
new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-realm.ini");
//2、得到SecurityManager实例 并绑定给SecurityUtils
org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//3、得到Subject及创建用户名/密码身份验证Token(即用户身份/凭证)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("benzhu", "123");
try {
//4、登录,即身份验证
subject.login(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
System.out.println("验证失败!");
//5、身份验证失败
}
System.out.println("11111!");
Assert.assertEquals(true, subject.isAuthenticated()); //断言用户已经登录
//6、退出
subject.logout();
}
}
评论